SEO Multilingue: Optimization FR/EN for SMEs
Multilingual SEO: Optimization FR/EN for SMEs
You are a Swiss SME and want to increase your online visibility? Bilingual SEO is the key to reaching both French and English speakers in Switzerland. With 23% of the population speaking French and a strong presence of English-speaking professionals, ignoring these languages could cost you clients. Here are the essential points to succeed in your bilingual SEO strategy:
- Target locally: Use hreflang tags (
fr-CH,en-CH) to avoid display errors on Google and prioritize a.chdomain. - Translation ≠ Localization: Adapt your content to cultural and linguistic specificities. For example, in French-speaking Switzerland, use local terms like "natel" or "septante".
- Site structure: Opt for clear subdirectories (
site.ch/fr/andsite.ch/en/) to maintain the authority of your domain. - Keyword research: Analyze locally searched terms, such as "web agency Geneva" (1,200 searches per month), instead of translating directly from English.
- Technical SEO: Ensure fast loading speed, mobile compatibility, and canonical tags for each language.
Bilingual SEO can help you conquer local and international markets while strengthening your credibility with Swiss consumers. Ready to take your site to the next level?
International SEO: The method to position your site in any country
The basics of multilingual SEO
To navigate effectively through the challenges of bilingual SEO, focus on three key elements: localization, hreflang tags, and duplicate content management.
Let's start with the distinction between translation and localization. Translation is limited to converting words from one language to another. Localization, on the other hand, goes further: it adapts content to the emotional context and cultural expectations of your audience. As Isaline Muelhauser explains (Pilea.ch):
If you only translate word for word, you risk losing the essence of your brand. The emotional impact, tone, trust - all of this can be lost in translation. [2]
Next, there are hreflang tags, which help Google understand which language version to show based on the user's location. For example, hreflang="fr-CH" targets French speakers in Switzerland, while hreflang="en-CH" addresses English speakers in the same country. These tags must be reciprocal: if your French page points to the English one, the English version must also link back to the French one.
Translation vs. localization
Localization is not just about translating; it also includes adapting local formats, such as Swiss franc amounts (CHF 1,234.50) or dates (14.05.2025). The tone and style should also match regional expectations: in French, opt for a fluid and elegant style; in English, prioritize clarity and structure. To succeed in this adaptation, rely on native speakers living in the targeted region. This ensures accuracy not only in translation but also in keyword research and content writing [2].
How do hreflang tags work
Hreflang tags are added in the HTML header or in an XML sitemap. For small and medium Swiss businesses (SMEs), a structure with subdirectories (e.g., site.ch/fr/ and site.ch/en/) is recommended. This method maintains the authority of your domain while clearly separating language versions. Each page should include references to all its language variants, including an x-default tag for the default page. Without this configuration, Google could display the wrong version to your visitors. As emphasized by AGMC:
Google's algorithms are sensitive to regional language variations. If your content is not correctly localized, you risk Google serving a French page to a user in Zurich, or a German page to a user in Lugano. [1]
Preventing duplicate content issues
Duplicate content becomes a problem when Google interprets your bilingual pages as identical copies instead of translated versions. Hreflang tags help avoid this by indicating that these pages are intentional variations for specific audiences [3]. Avoid automatic redirects based on IP address or browser settings, as they prevent search engine bots from accessing all your language versions. Prefer a visible language selector, such as a menu or button, to allow users to manually choose their language [3]. If your site has many pages, use an XML sitemap to manage your hreflang tags: this simplifies maintenance and reduces the risk of technical errors.
With these strong foundations, you are ready to move on to the next step: practical optimization of bilingual SEO.
How to optimize bilingual SEO step by step
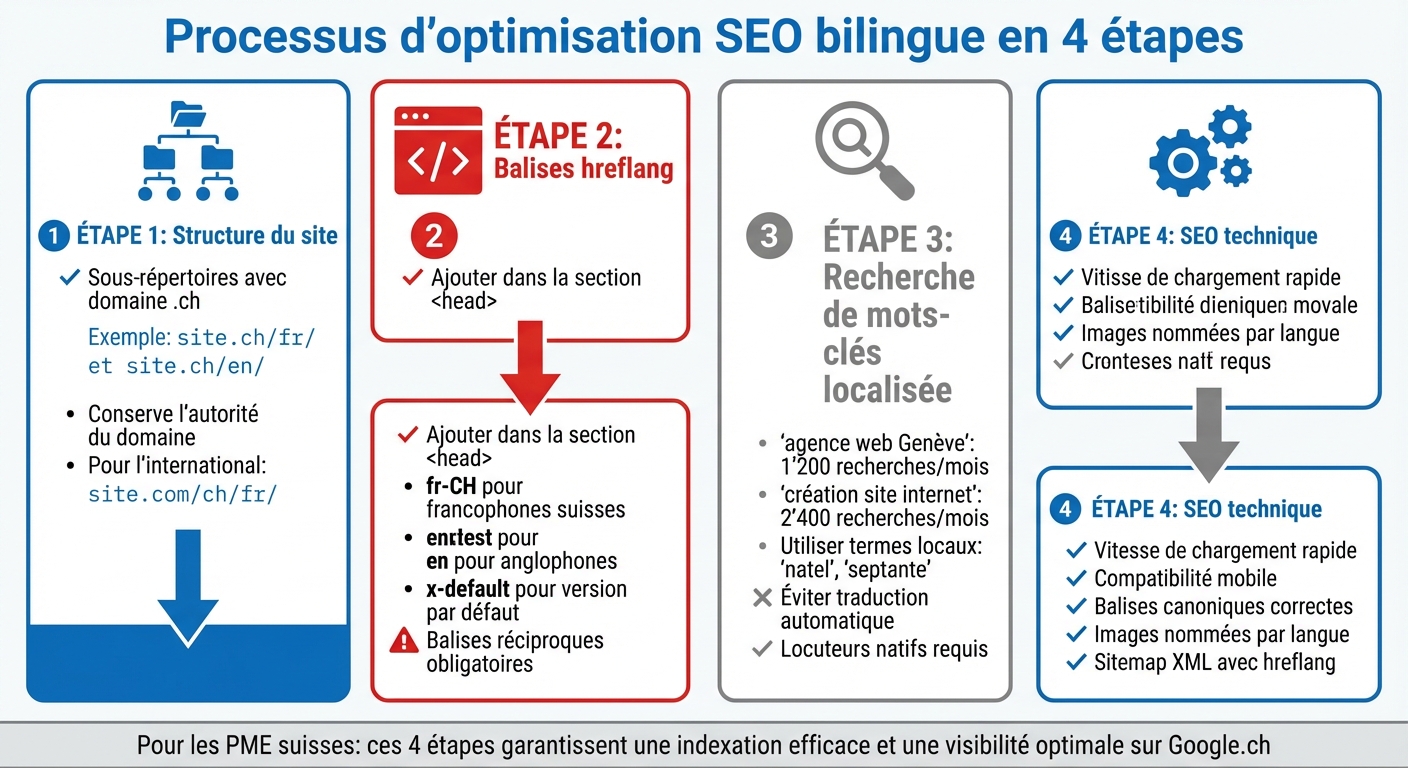
4 essential steps to optimize your bilingual FR/EN SEO in Switzerland
Let's now move on to concrete actions to improve the bilingual SEO of your site. This optimization is based on four main axes: site structure, hreflang tags, keyword research, and technical SEO. Each technical choice can directly influence your positioning on Google.ch.
Choosing your site structure
For a Swiss SME, opting for a structure with subdirectories with a .ch domain is often the ideal solution: site.ch/fr/ and site.ch/en/. This format allows you to maintain domain authority while clearly distinguishing language versions. If you also target an international audience, prefer a country-oriented structure, such as site.com/ch/fr/, rather than site.com/fr/ch/, to avoid diluting local authority [1].
Correctly configuring hreflang tags
Each page of your site should include hreflang tags in the <head> section to reference all its language variants. Here's an example for a Swiss site with versions in French and English:
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="fr-CH" href="https://www.site.ch/fr" />
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="en" href="https://www.site.ch/en" />
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="x-default" href="https://www.site.ch" />
The x-default tag indicates the default version for users whose language does not match any of the available versions. Attention: if you already use site.com/fr/ for France, avoid adding site.com/fr/ch/ for Switzerland, as this could lead to cannibalization of results in search engines [1].
Keyword research for each language
Translating keywords literally is a common mistake. In Switzerland, "natel" is used to refer to a mobile phone, while in France, "portable" is used [4]. These nuances highlight the importance of thorough local research. Analyze search volumes specific to Switzerland: for example, "web agency Geneva" attracts 1,200 monthly searches, while "website creation" generates 2,400 [4]. Avoid automatic translation for your keywords. Only native speakers can identify local expressions and formulations that build trust [4]. Also, remember to adapt your meta-titles, meta-descriptions, and alt tags to capture search intentions in each language [4].
Technical SEO for bilingual sites
Ensure that your site meets technical basics: fast loading speed, mobile compatibility, and correctly configured canonical tags. Each page should include a canonical tag that points to itself. For images, use file names adapted to each language (e.g., web-agency-geneva.jpg) and compress them for optimized performance. Finally, update your XML sitemap to include all hreflang variants. These technical adjustments ensure effective indexing of your bilingual content and strengthen the foundation for developing a solid backlinking strategy.
sbb-itb-454261f
Creating backlinks in multiple languages
Backlinks function as recommendations: a link from a site in French-speaking Switzerland primarily enhances your French version, while a link in English supports your English version. These strategies play a key role in bilingual SEO. For Swiss SMEs, this distinction is essential. Julien Vidal, SEO consultant, summarizes it as follows:
A backlink from a site in French-speaking Switzerland will have less added value for the services you offer in German-speaking Switzerland. Ideally, get recommendations in each region. [5]
Let's now explore concrete methods to obtain these valuable links.
Link acquisition methods by language
Start by mobilizing your local partners in each language region. For example, a satisfied customer in Geneva can recommend your site in French, while a collaborator in Zurich could link to your English version. This method is particularly suitable for SMEs.
Adapt your content to local preferences: offer case studies or stories for French speakers, and technical guides for English speakers [1]. Avoid automatic translations, which can harm the credibility of your recommendations.
Leveraging local events and media to obtain links
Once your partners are activated, also take advantage of local events. Participate in trade shows or conferences in different regions and document your presence in both languages. For example, speaking at a trade show in Geneva can earn you mentions in the French-speaking local press, while a conference in Zurich can open the door to English backlinks.
Contact cantonal economic newspapers and offer them content tailored to their audience: economic analyses for French-speaking media and technical guides for English publications. These efforts enhance your visibility and increase your chances of obtaining links.
Partnerships with local organizations are another source of relevant links. By sponsoring community events in different cantons, you can obtain backlinks from sites in the appropriate language. Be vigilant about the quality of sources: search engines penalize unnatural link exchanges or purchases [5].
By combining these approaches and customizing your efforts for each language market, Swiss SMEs can optimize their bilingual SEO. To deepen your SEO strategy in French and English, seek the expertise of ().
Tracking and improving bilingual SEO results
Once your SEO strategy is in place, it is crucial to measure the performance of each language version. Without precise data, it's difficult to know if your efforts are paying off or if adjustments are needed for a specific language.
Configuring analysis tools for multiple languages
In Google Analytics, segment your data by language and region. Create separate views for your French and English versions to track user behavior separately. For example, use cookies or local storage to remember visitors' language preference, enhancing their experience.
Ensure your hreflang tags are correctly configured. Tools like Google Search Console, Ahrefs, or Screaming Frog can detect potential errors. While automatic detection is useful, a visible manual language selector remains essential to correct any inconsistencies. These steps will help you obtain reliable data to analyze your performance.
Key indicators for bilingual SEO
For each language, focus on specific metrics. For example, the organic traffic of your French version can be segmented by canton (Geneva, Vaud, etc.), while your English version targets an international audience, including expatriates. Also, analyze the conversion rate and bounce rate for each language region.
| Metric | French version (FR-CH) | English version (EN) |
|---|---|---|
| Organic traffic |
