SEO geolocated for LLMs: Guide 2026
Geolocalized SEO for LLMs: Guide 2026
In 2026, local searches no longer necessarily end with a click on a website. Approximately 60 to 63% of users find their answer directly through AIs like ChatGPT or Google Gemini. For Swiss companies, being mentioned by these models has become a priority.
Here is what you need to know:
-
What is it?
Optimize your content so that AIs recognize you as a reliable local source and mention you in their responses. -
Why is it important?
Local searches on smartphones lead to quick actions: 78% result in a store visit within 24 hours. AIs synthesize conversational responses based on criteria like proximity and relevance. -
Who benefits?
Restaurants, medical practices, luxury boutiques, fintech startups, and many other local sectors. -
How to succeed?
- Create clear and concise content (40-60 words).
- Use Schema.org markup (
LocalBusiness,FAQ). - Ensure linguistic consistency (FR/EN) and local formatting (CHF, dates, hours).
Quick comparison of SEO approaches:
| Criterion | General SEO | Geolocalized SEO (GEO) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Objective | SERP ranking | Local visibility | Mention by AI |
| Tactics | Keywords, backlinks | Google Business, NAP | Structured data |
| Success measurement | CTR, position | Store visits | Mention frequency |
For Swiss companies, integrating GEO is no longer an option but a necessity to remain visible in an AI-driven world.
This AEO/GEO/LLMO/SEO Bruh WTF? Strategy Explained for 2026 (How to rank in AI for local businesses)
Traditional SEO vs. Local SEO vs. GEO
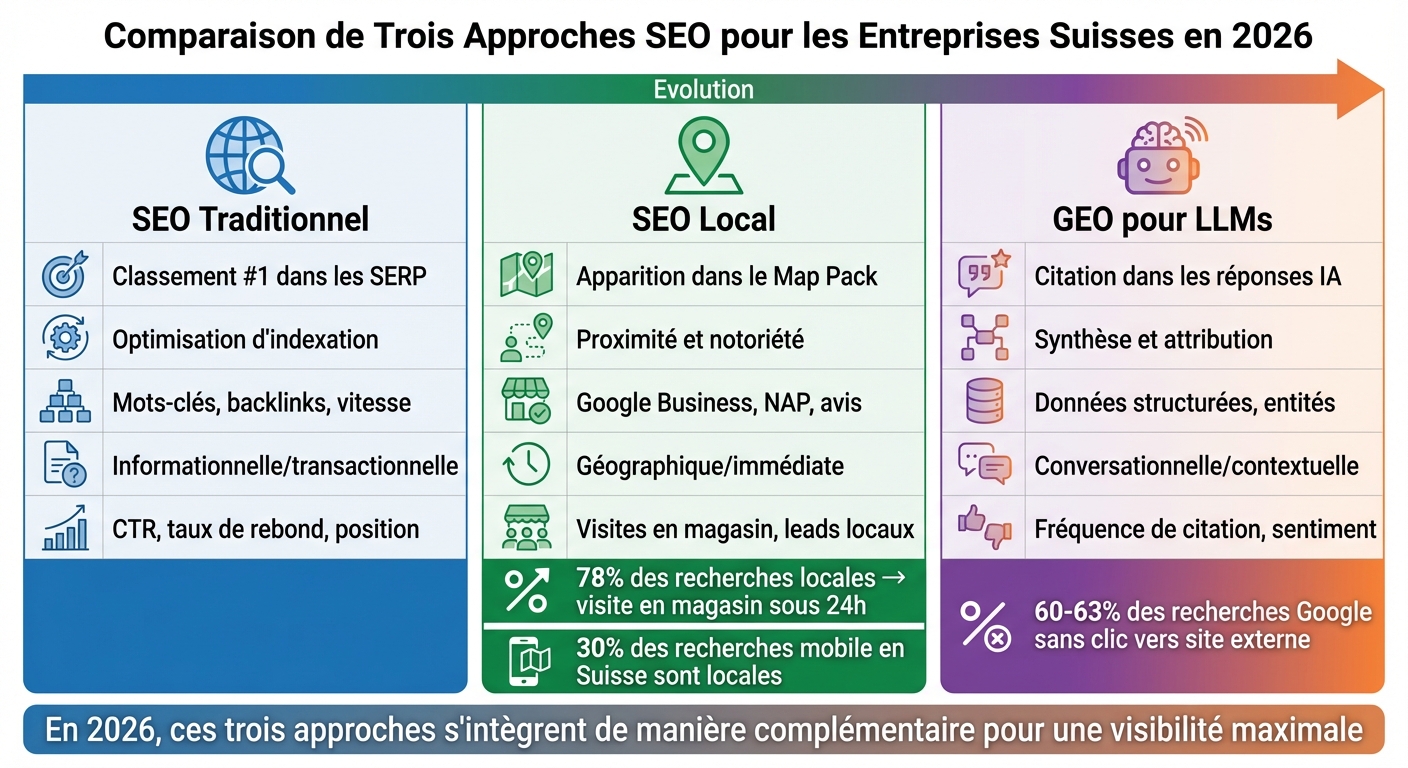
Comparison vs Local SEO vs GEO for LLMs in 2026
To fully understand the GEO, it is essential to position it in relation to more traditional approaches. These three strategies – Traditional SEO, Local SEO, and GEO – respond to distinct logics. Traditional SEO aims for optimal ranking in general search results, Local SEO focuses on geographical proximity, and GEO stands out by specifically targeting integration into responses generated by artificial intelligence. Here is a detailed overview of these approaches to better grasp their differences and complementarities.
Traditional SEO: aiming for global visibility
Traditional SEO is based on three fundamental pillars: keywords, backlinks, and the technical performance of the site [1]. The goal is simple: to appear at the top of search result pages (SERP) for general queries like "Swiss web agency" or "digital marketing." Performance is measured using indicators such as click-through rate (CTR), bounce rate, and position in the results [1].
This approach is ideal for general content where geographical scope is not a key factor.
Local SEO: capitalizing on proximity
Local SEO, on the other hand, relies on three main criteria: proximity (distance between the user and the business), local notoriety (popularity and customer reviews), and relevance (alignment with user queries) [3]. Tactics include optimizing your , ensuring consistency of NAP information (name, address, phone) on platforms like local.ch and search.ch, as well as [3].
The numbers speak for themselves: in Switzerland, 30% of mobile searches have a local dimension, and 78% of these searches result in a store visit within 24 hours [3]. These elements highlight the importance of local SEO to attract a local clientele and pave the way for GEO optimization.
GEO for LLMs: optimizing content for artificial intelligence
With the emergence of artificial intelligence, GEO (Generative Engine Optimization) redefines the rules of the game. Unlike traditional algorithms that rank pages, language models (LLMs) analyze dozens of sources, extract relevant information, and synthesize a unique response [4]. In this scenario, your content is no longer just a clickable result but an element directly integrated into a response generated by AI [4].
To succeed in this new era, GEO relies on structured data (such as those defined by Schema.org), clear entities, and concise excerpts designed to be easily integrated into AI responses [4] [5]. Success metrics also differ: they are now measured by mention frequency and the sentiment associated with your brand in the generated responses [1] [4].
| Criterion | Traditional SEO | Local SEO | GEO for LLMs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Main objective | #1 ranking in SERP [1] | Appearance in Map Pack [3] | Mention in AI responses [4] |
| Basic logic | [4] | Proximity and notoriety [3] | Synthesis and attribution [4] |
| Key tactics | Keywords, backlinks, speed [1] | Google Business, NAP, reviews [3] | Structured data, entities [5] |
| Type of query | Informational/transactional [4] | Geographical/immediate [3] | Conversational/contextual [4] |
| Success metric | CTR, bounce rate, position [1] | Store visits, local leads [3] | Mention frequency, sentiment [1] [4] |
In 2026, these three approaches integrate complementarily. For Swiss companies wishing to remain visible in an increasingly AI-dominated world, GEO is an essential lever.
Best GEO Practices for Swiss Companies
Let's move on to concrete recommendations for Swiss companies. To succeed in your GEO strategy, it is crucial to structure your content in a way that is easily exploitable by artificial intelligence (AI) models. The main goal of GEO is to be mentioned by these models, rather than just appearing in search results. Here are three essential axes to achieve this in Switzerland.
Optimization for a bilingual FR/EN audience
In Switzerland, bilingualism is an unavoidable reality: your content must be available in French and English, while respecting regional preferences. It starts with the use of hreflang tags, which allow search engines and AI models to present the appropriate language version to each user. Regarding URL structure, here are three possible options:
| URL Structure | Strengths | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
Subdirectories (/fr/, /en/) |
Simplified management and consolidated SEO authority | No localized hosting |
Subdomains (fr.site.ch) |
Clear separation and | Divided SEO authority |
Distinct domains (.ch) |
Optimized local signal | Higher costs and complex management |
But beware, translation alone is not enough. Your content must also be adapted to local specificities. For example, use CHF 1'234.50 for amounts, 14.05.2025 for dates, and 14h30 for hours in French (or 14:30 in English). These adjustments enhance your credibility and facilitate the interpretation of information by AI models. Careful linguistic preparation is the basis of effective technical structuring, which we will address next.
Using Schema Markup for Local Businesses
Structured data is the preferred language of AI models. In 2026, integrating Schema.org becomes essential to maximize your chances of being mentioned. Schema types to prioritize include LocalBusiness, FAQ, HowTo, Product, and Organization, which immediately contextualize your content [4].
For the LocalBusiness schema, ensure that your NAP details (name, address, phone) are consistent across all platforms, whether it's your site, local.ch, search.ch, or other business directories [3]. A clear format validated by AI models is essential. Additionally, adhering to local and cultural standards enhances your legitimacy with users and LLMs.
Respecting Swiss Cultural and Legal Standards
Switzerland
